Any links to online stores should be assumed to be affiliates. The company or PR agency provides all or most review samples. They have no control over my content, and I provide my honest opinion.
This article was originally published on Make the Sound Better. While I have updated most of the articles that have been transferred over, this article is mostly unedited.
Introduction: Understanding Microphone Polar Patterns
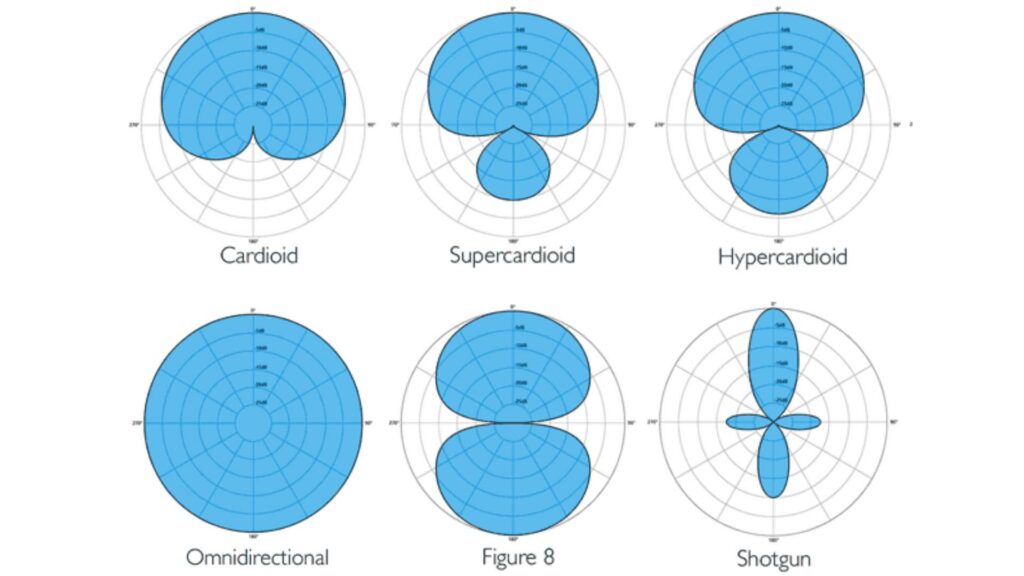
Microphone polar patterns refer to the way in which a microphone captures sound in relation to its position. Different polar patterns are suited for different recording situations and can drastically affect the quality of the recorded sound. Understanding the polar patterns is crucial for achieving the desired sound quality when recording audio.
Omnidirectional: Capturing Sound from All Directions
Omnidirectional microphones capture sound equally from all directions. They are ideal for recording ambient sounds or group performances where the sound needs to be captured from all directions. Omnidirectional microphones have a spherical or hemispherical pickup pattern and are commonly used in recording concerts, orchestras, and choirs.
Cardioid: Ideal for Solo Performers and Podcasters
Cardioid microphones capture sound from the front, but are less sensitive to sounds from the sides and rear. They are ideal for solo performances or podcasting, where the focus is on capturing the voice of the performer or speaker. Cardioid microphones have a heart-shaped pickup pattern and are commonly used in recording vocals, acoustic guitars, and podcasts.
Supercardioid: A Tighter Focus on Sound Sources
Supercardioid microphones have a narrower pickup pattern than cardioid microphones, making them ideal for situations where the sound source needs to be isolated. They are commonly used in live performances, broadcasting, and recording in noisy environments. Supercardioid microphones have a tighter heart-shaped pickup pattern than cardioid microphones and are ideal for recording vocals, drums, and guitars.
Hypercardioid: Narrowing in on Specific Sounds
Hypercardioid microphones have an even narrower pickup pattern than supercardioid microphones, making them ideal for recording specific sounds. They are commonly used in recording dialogues, voiceovers, and interviews. Hypercardioid microphones have an elongated heart-shaped pickup pattern and are ideal for recording vocals, guitar amps, and drums.
Bidirectional: Perfect for Interviews and Duets
Bidirectional microphones capture sound from the front and back, but not from the sides. They are ideal for recording interviews, duets, and capturing sound in reflective environments. Bidirectional microphones have a figure-8 pickup pattern and are commonly used in recording interviews, podcasts, and voiceovers.
Shotgun: Capturing Sound from Long Distances
Shotgun microphones capture sound from a narrow directionality, making them ideal for capturing sound from long distances. They are commonly used in film and television production and for recording wildlife sounds. Shotgun microphones have a long, narrow pickup pattern and are ideal for recording vocals, sound effects, and instruments in noisy environments.
Subcardioid: A Combination of Cardioid and Omnidirectional
Subcardioid microphones capture sound from the front and sides but less from the rear. They are ideal for recording ambient sounds or live performances where the performers move around the stage. Subcardioid microphones have a wide pickup pattern with a slight heart shape and are commonly used in recording live performances, choirs, and orchestras.
Figure-8: Recording from Front and Back Simultaneously
Figure-8 microphones capture sound equally from the front and back but not from the sides. They are ideal for recording duets, interviews, and capturing sound in reflective environments. Figure-8 microphones have a figure-8 pickup pattern and are commonly used in recording podcasts, voiceovers, and interviews.
Multi-Pattern: Flexibility for Different Recording Situations
Multi-pattern microphones allow for different polar patterns to be selected, making them ideal for recording a variety of sounds. They are commonly used in recording studios and live performances where the sound needs to be captured from different directions. Multi-pattern microphones have different polar patterns such as cardioid, omnidirectional, and bidirectional, and are ideal for recording vocals, drums, and guitars.
Top 10 Microphones with Different Polar Patterns
| Microphone | Polar Pattern | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Rode NT1-A | Cardioid | Vocals, Acoustic Guitars, Podcasts |
| Audio-Technica AT4053B | Hypercardioid | Vocals, Guitars, Drums |
| Shure SM7B | Cardioid | Vocals, Podcasts, Broadcast |
| Neumann U87 AI | Multi-Pattern | Vocals, Piano, Guitar |
| Sennheiser MK8 | Multi-Pattern | Vocals, Guitars, Drums |
| Rode NTG3 | Supercardioid | Film, Television, Wildlife Recording |
| AKG C414 XLII | Multi-Pattern | Vocals, Drums, Guitars |
| Shure KSM9 | Supercardioid | Live Performances, Vocals |
| Sennheiser e965 | Cardioid | Live Performances, Vocals |
| Audio-Technica AT4050 | Multi-Pattern | Vocals, Drums, Guitars |
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Microphone for Your Needs
Choosing the right microphone polar pattern is crucial for achieving the desired sound quality when recording audio. Different polar patterns are suited for different recording situations, and selecting the right one can make a significant difference in the quality of the recording. Consider your recording environment, the type of sound you want to capture, and the equipment you have available when selecting a microphone with a specific polar pattern. With the right microphone polar pattern, you can achieve high-quality audio recordings.
I am James, a UK-based tech enthusiast and the Editor and Owner of Mighty Gadget, which I’ve proudly run since 2007. Passionate about all things technology, my expertise spans from computers and networking to mobile, wearables, and smart home devices.
As a fitness fanatic who loves running and cycling, I also have a keen interest in fitness-related technology, and I take every opportunity to cover this niche on my blog. My diverse interests allow me to bring a unique perspective to tech blogging, merging lifestyle, fitness, and the latest tech trends.
In my academic pursuits, I earned a BSc in Information Systems Design from UCLAN, before advancing my learning with a Master’s Degree in Computing. This advanced study also included Cisco CCNA accreditation, further demonstrating my commitment to understanding and staying ahead of the technology curve.
I’m proud to share that Vuelio has consistently ranked Mighty Gadget as one of the top technology blogs in the UK. With my dedication to technology and drive to share my insights, I aim to continue providing my readers with engaging and informative content.







